Judicial Recusals: Safeguarding Legal Impartiality
Introduction: In the realm of justice, impartiality stands as a cornerstone. Judicial recusals, a critical yet often overlooked aspect of legal proceedings, play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of our courts. This article delves into the intricacies of recusal practices, exploring their significance, challenges, and impact on the justice system.
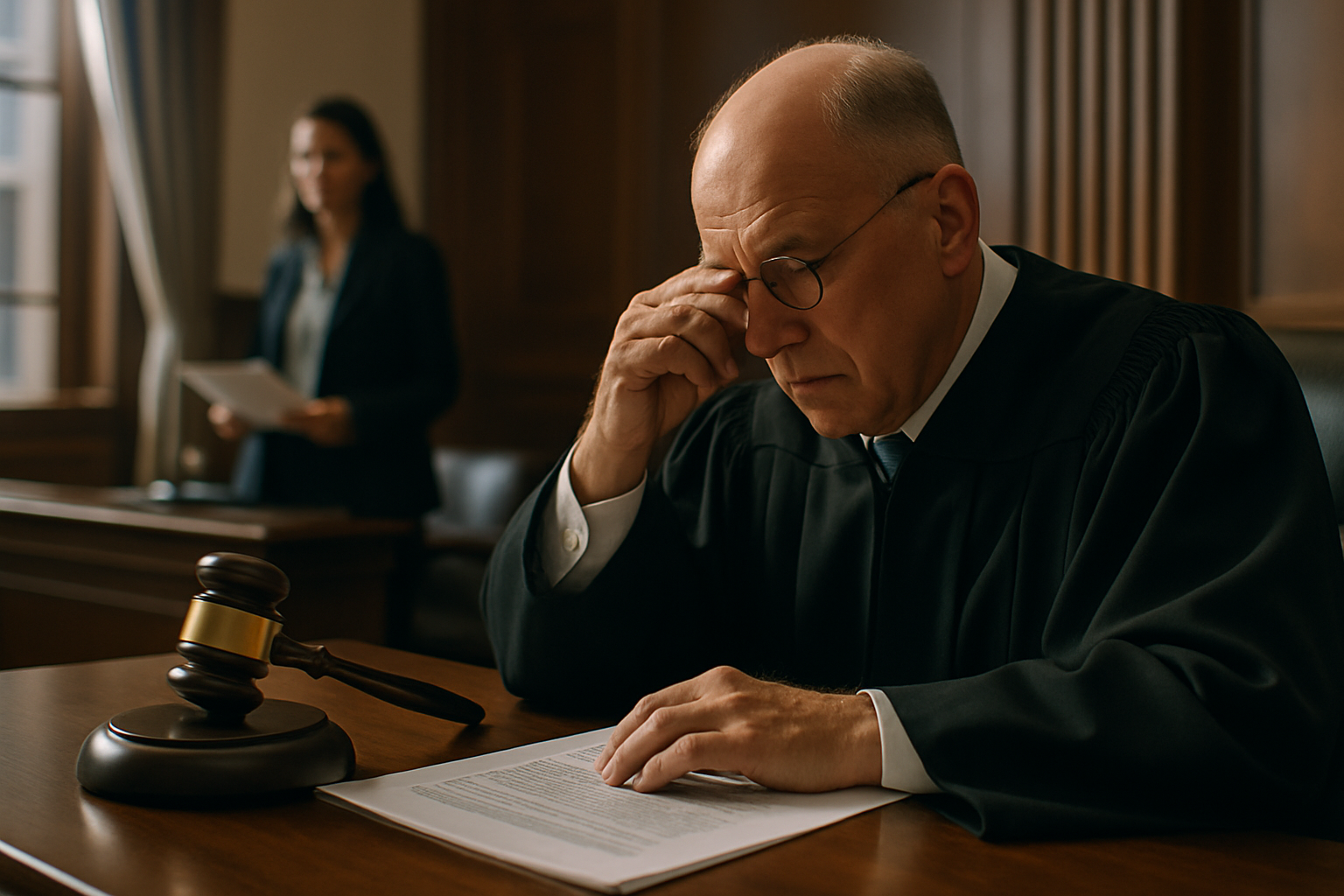

Historical Context of Judicial Recusals
The concept of judicial recusal dates back to ancient legal systems, where the principle of nemo iudex in causa sua (no one should be a judge in their own case) was established. In common law jurisdictions, the practice evolved gradually, with early English courts recognizing the need for judges to step aside in cases where they had a direct interest. The United States adopted and expanded these principles, codifying recusal standards in federal law and judicial codes of conduct.
Legal Framework Governing Recusals
In the United States, judicial recusals are governed by both statutory law and ethical guidelines. The federal recusal statute, 28 U.S.C. § 455, outlines specific circumstances under which judges must disqualify themselves. These include personal bias or prejudice, financial interests, and prior involvement with a case. Additionally, the Code of Conduct for United States Judges provides ethical standards that supplement the statutory requirements, emphasizing the importance of avoiding even the appearance of impropriety.
Grounds for Recusal
Judges may recuse themselves for various reasons. Common grounds include financial interests in the case outcome, personal relationships with parties or attorneys, prior involvement with the case in a different capacity, or public statements that might suggest bias. The standard for recusal is not just actual bias but also the appearance of bias, recognizing that public perception of judicial impartiality is crucial for maintaining confidence in the legal system.
Challenges in Implementing Recusal Practices
Despite clear guidelines, the implementation of recusal practices faces several challenges. One significant issue is the subjective nature of determining when recusal is necessary. Judges must often make difficult decisions about whether their circumstances create an appearance of bias, even if they believe they can remain impartial. Additionally, in smaller jurisdictions or specialized courts, finding an unbiased judge without any connections to the case can be challenging.
Impact on Legal Proceedings and Public Trust
Judicial recusals can have significant impacts on legal proceedings. They may cause delays, increase costs, and in some cases, alter the outcome of a case. However, these short-term disruptions are generally viewed as necessary to maintain the long-term integrity of the judicial system. Proper recusal practices enhance public trust in the courts by demonstrating a commitment to fairness and impartiality. Conversely, failures to recuse in appropriate situations can erode public confidence and lead to questions about the legitimacy of judicial decisions.
Recent Developments and Controversies
In recent years, judicial recusals have gained increased attention, particularly in high-profile cases involving Supreme Court justices. Debates have arisen over whether the current recusal standards are sufficient, especially given the unique position of Supreme Court justices who are not subject to review by a higher court. Some legal scholars and lawmakers have called for more stringent recusal rules or external review processes for recusal decisions at the highest levels of the judiciary.
The Role of Technology in Recusal Practices
Advancements in technology are beginning to play a role in recusal practices. Electronic filing systems and conflict-checking software can help identify potential conflicts of interest more efficiently. However, these tools also raise new questions about privacy and the extent to which judges’ personal and financial information should be accessible for conflict-checking purposes.
International Perspectives on Judicial Recusals
Examining judicial recusal practices in other countries provides valuable insights and potential areas for improvement in the U.S. system. Some jurisdictions have adopted more formalized processes for recusal decisions, including external review mechanisms. Others have implemented stricter disclosure requirements for judges. Comparing these approaches can inform discussions about best practices and potential reforms in the American legal system.
Future of Judicial Recusals
As the legal landscape evolves, so too must recusal practices. Future developments may include more comprehensive disclosure requirements for judges, standardized procedures for handling recusal requests, and potentially, the use of artificial intelligence to assist in identifying conflicts of interest. Balancing the need for transparency and accountability with the protection of judicial independence will remain a key challenge in shaping the future of recusal practices.
In conclusion, judicial recusals serve as a critical mechanism for maintaining the integrity and impartiality of the legal system. While challenges exist in their implementation, continued attention to this issue, along with thoughtful reforms and adaptations to changing circumstances, will be essential in preserving public trust in the judiciary. As legal professionals and citizens alike, understanding and supporting effective recusal practices is crucial for the health of our democratic institutions and the pursuit of justice.