Miniaturization Trends in Advanced Circuitry
The relentless drive towards smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient electronic devices continues to reshape our world. Miniaturization in advanced circuitry represents a fundamental shift in how technology is designed and implemented, impacting everything from consumer electronics to industrial applications. This ongoing trend enables unprecedented capabilities, allowing complex systems to fit into ever-diminishing spaces while enhancing overall performance and functionality across a vast array of modern technologies.
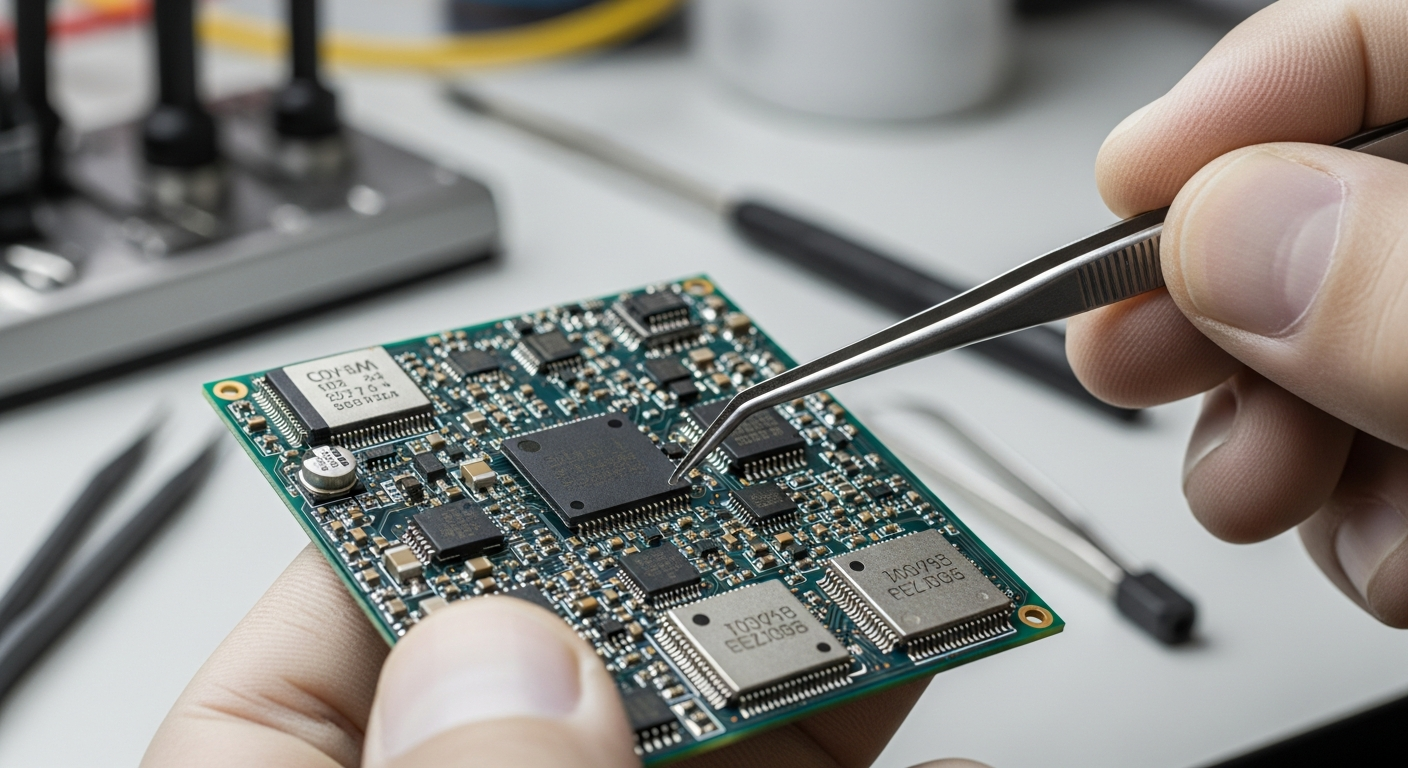
The ongoing evolution of electronics is largely characterized by a persistent push for miniaturization. This trend, deeply rooted in the principles of advanced circuitry, has been a primary catalyst for innovation across various sectors, enabling the development of sophisticated computing systems, compact hardware, and a diverse range of devices that are both powerful and portable. Understanding the forces driving this reduction in size, alongside its implications, is crucial for appreciating the trajectory of modern technology.
The Driving Force Behind Miniaturization in Electronics
The demand for more compact, faster, and less power-consuming electronics fuels the miniaturization trend. This drive stems from consumer desire for sleeker gadgets, the need for enhanced functionality in limited spaces, and the pursuit of greater efficiency in all technological applications. Innovations in manufacturing processes and materials have allowed engineers to pack more transistors onto a single chip, leading to significant boosts in computing power without increasing physical size. This quest for greater density and performance per square millimeter is a core aspect of modern technology development.
Key Technological Advancements in Circuitry and Materials
Progress in miniaturization relies heavily on breakthroughs in semiconductor fabrication and the introduction of novel materials. Modern circuits are created using lithography techniques that can etch features at the nanometer scale, pushing the boundaries of what was previously thought possible. Advanced packaging technologies, such as 3D stacking of chips, further contribute to this trend by allowing multiple components to be integrated vertically, drastically reducing the overall footprint of hardware. The exploration of new materials, including two-dimensional materials like graphene, also promises to unlock even greater levels of miniaturization and efficiency in future electronics.
Impact on Modern Devices and Wearables
Miniaturization has profoundly transformed the landscape of modern devices, making possible the ubiquitous smartphones, smartwatches, and other wearables that define contemporary life. Smaller components mean that more powerful computing capabilities can be integrated into portable forms, leading to highly functional devices. This has also enabled the proliferation of sophisticated sensors in everyday objects, contributing to the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT). Furthermore, advances in miniaturized displays are leading to more immersive and flexible visual interfaces, enhancing user interaction with these compact devices.
Miniaturization’s Role in AI and Advanced Connectivity
The ability to integrate complex circuits into tiny packages is critical for the advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and high-speed connectivity. Miniaturized, specialized AI processors can now be embedded directly into devices, enabling on-device machine learning capabilities without constant reliance on cloud computing. This not only enhances privacy by processing data locally but also reduces latency and improves responsiveness. Similarly, the compact nature of modern radio frequency (RF) circuits is essential for developing next-generation connectivity standards, such as 5G and future wireless protocols, facilitating faster and more reliable data transfer in increasingly smaller form factors.
Considerations for Sustainability and Modular Design
While miniaturization offers numerous benefits, its environmental implications and potential for sustainability are important considerations. The production of increasingly complex, tiny circuits often requires specialized resources and energy. However, smaller devices can also lead to reduced material consumption and lower energy usage during operation, contributing to overall efficiency. The concept of modular design, where components can be easily upgraded or replaced, is gaining traction as a way to extend the lifespan of electronics, counteracting the potential for rapid obsolescence often associated with highly integrated, miniaturized systems. This approach seeks to balance innovation with environmental responsibility.
The ongoing trends in miniaturization continue to redefine the capabilities and form factors of electronics. From enabling more powerful computing in smaller packages to facilitating the growth of AI and advanced connectivity, the impact is widespread. As researchers and engineers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible at the nanoscale, the future promises even more innovative, efficient, and integrated technological solutions, shaping how individuals interact with the digital world and beyond.






